Chevrolet Sonic Repair Manual: Crankcase Ventilation System Inspection/Diagnosis
- Results of Incorrect Operation
-
A plugged positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) orifice or hose may cause the following conditions:
- Rough idle
- Stalling or slow idle speed
- Oil leaks
- Oil in the throttle body
- Sludge in the engine
- Functional Check
-
With these systems, any blow-by in excess of the system capacity, from a badly worn engine, sustained heavy load, etc., is exhausted into the throttle body and is drawn into the engine.
Proper operation of the crankcase ventilation system depends upon a sealed engine. If oil slugging or dilution is noted and the crankcase ventilation system is functioning properly, check the engine for a possible cause. Correct any problems.
If an engine is idling rough, inspect for a clogged PCV orifice, a dirty vent filter, air cleaner element, or plugged hose. Replace as required. Use the following procedure:
- Remove the PCV hose from the cylinder head cover.
- Operate the engine at idle.
- Place your thumb over the end of the hose in order to check for a vacuum. If there is no vacuum at the hose, inspect for the following items:
- Plugged hoses
- The manifold port
- Turn OFF the engine.
- Inspect the PCV orifice in the cylinder head cover for debris or blockage.
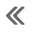 PCV
PCV
...
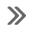 Positive Crankcase Ventilation Hose/Pipe/Tube Replacement
Positive Crankcase Ventilation Hose/Pipe/Tube Replacement
Removal Procedure
Remove the air cleaner outlet duct. Refer to Air Cleaner Outlet Duct
Replacement.
Open the 2 positive crankcase ventilation pipe retainer clips ...
Other materials:
Body Waterleak Repair
Warning: If the vehicle interior is exposed to moisture and becomes
soaked up to the level of the sensing and diagnostic module (SDM), the SDM and
SDM harness connector must be replaced. The SDM could be activated when powered,
which could cause airbag deployment and result in person ...
Headlining Trim Panel Replacement (Sedan with Sunroof)
Headlining Trim Panel Replacement
Callout
Component Name
Warning: Do not attempt to repair or alter the head impact
energy-absorbing material glued to the headliner or to the garnish trims.
If the material is damaged ...
Engine Coolant Fan Shroud Replacement (LDE LUW)
Engine Coolant Fan Shroud Replacement
Callout
Component Name
Preliminary Procedure
Remove the radiator surge tank. Refer to Radiator Surge Tank Replacement.
Unclip transmission cooler lines from shroud if equipped.
Un ...
0.0077
